In many universities and training centres, handwritten signatures and stamps are still used as symbols of document validation. Unfortunately, these practices are becoming increasingly vulnerable to forgery. Signatures can be photographed, copied manually or using AI, and reused on other documents without the knowledge of authorised parties.
The consequences go far beyond administrative issues. Forged documents undermine institutional trust, damage reputation, and threaten the credibility of academic records themselves.
For this reason, a more innovative and secure approach is required. One solution is the use of encrypted digital signatures embedded in QR codes (not standard QR codes), protected by GoValid’s Anti-Counterfeit system. Instead of relying on ink signatures, this system allows anyone to verify a document’s status instantly through scanning. Let us explore how it works and why it is significantly safer.
How QR Codes Function as Proof of Authenticity
Encrypted digital signatures embedded in QR codes serve as proof of authenticity by linking documents to verifiable digital records. In this system, documents are no longer signed manually. Instead, they are issued together with a unique QR code.
In GoValid, each user is assigned a unique digital key that acts as a personal digital fingerprint and cannot be duplicated. When the QR code is scanned, it directs the user to the official university or institutional server where the original document data is securely stored.
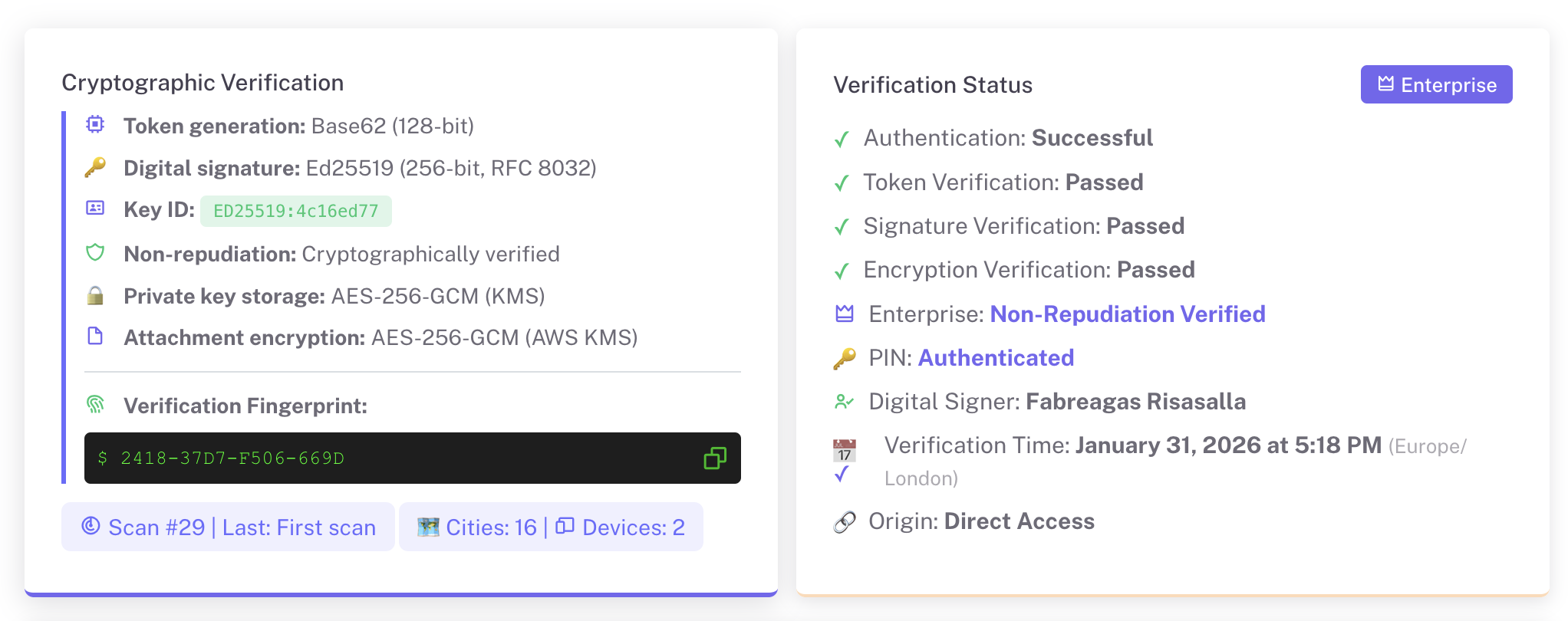
The verification page displays information such as the institution’s name, document number, and issuance date, matching the physical document. If the data aligns, the document is confirmed as valid.
This approach makes document forgery significantly more difficult than traditional handwritten signatures or image-based stamps.
The Role of GoValid Anti-Counterfeit in Detecting Academic Document Fraud
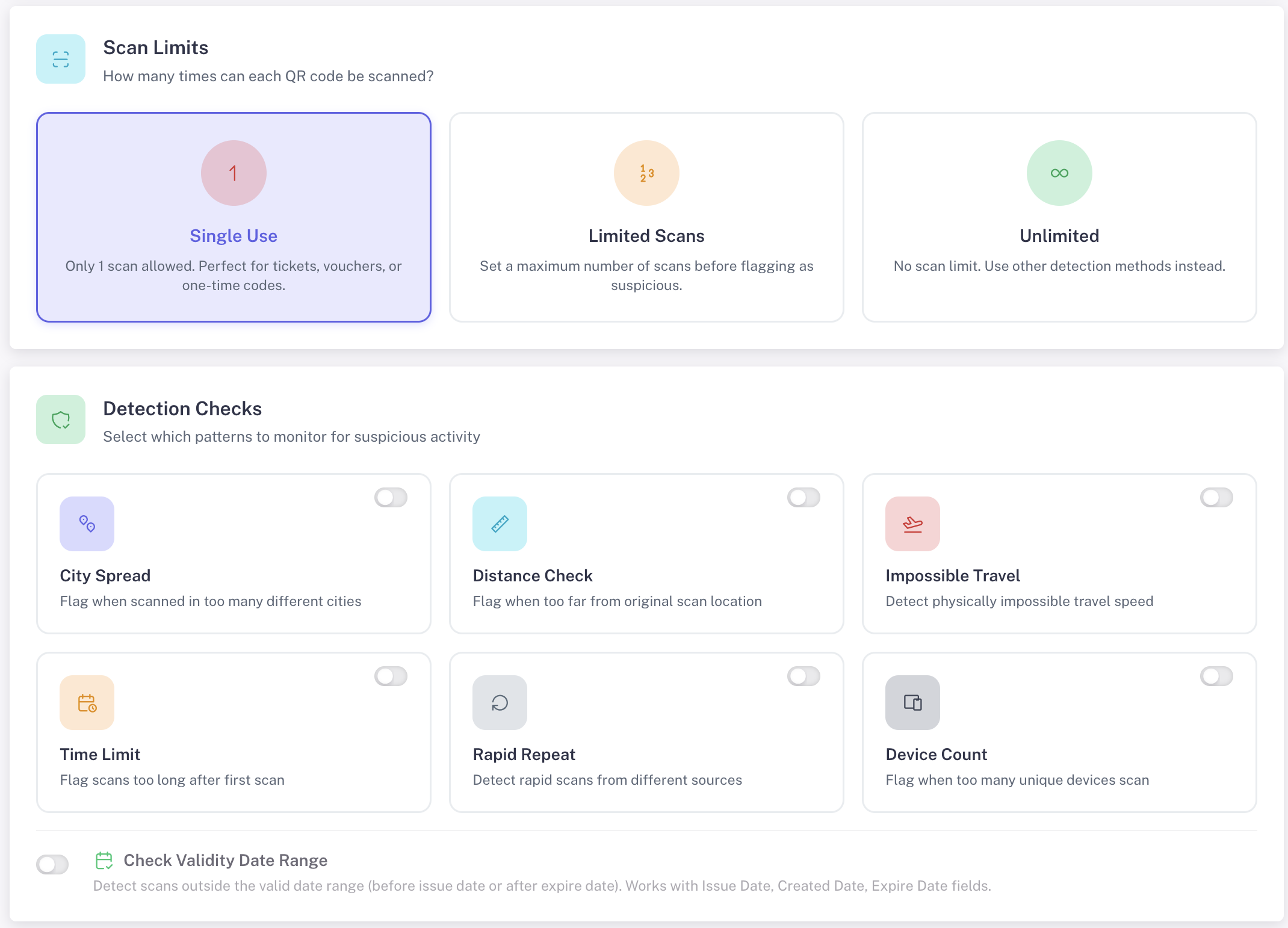
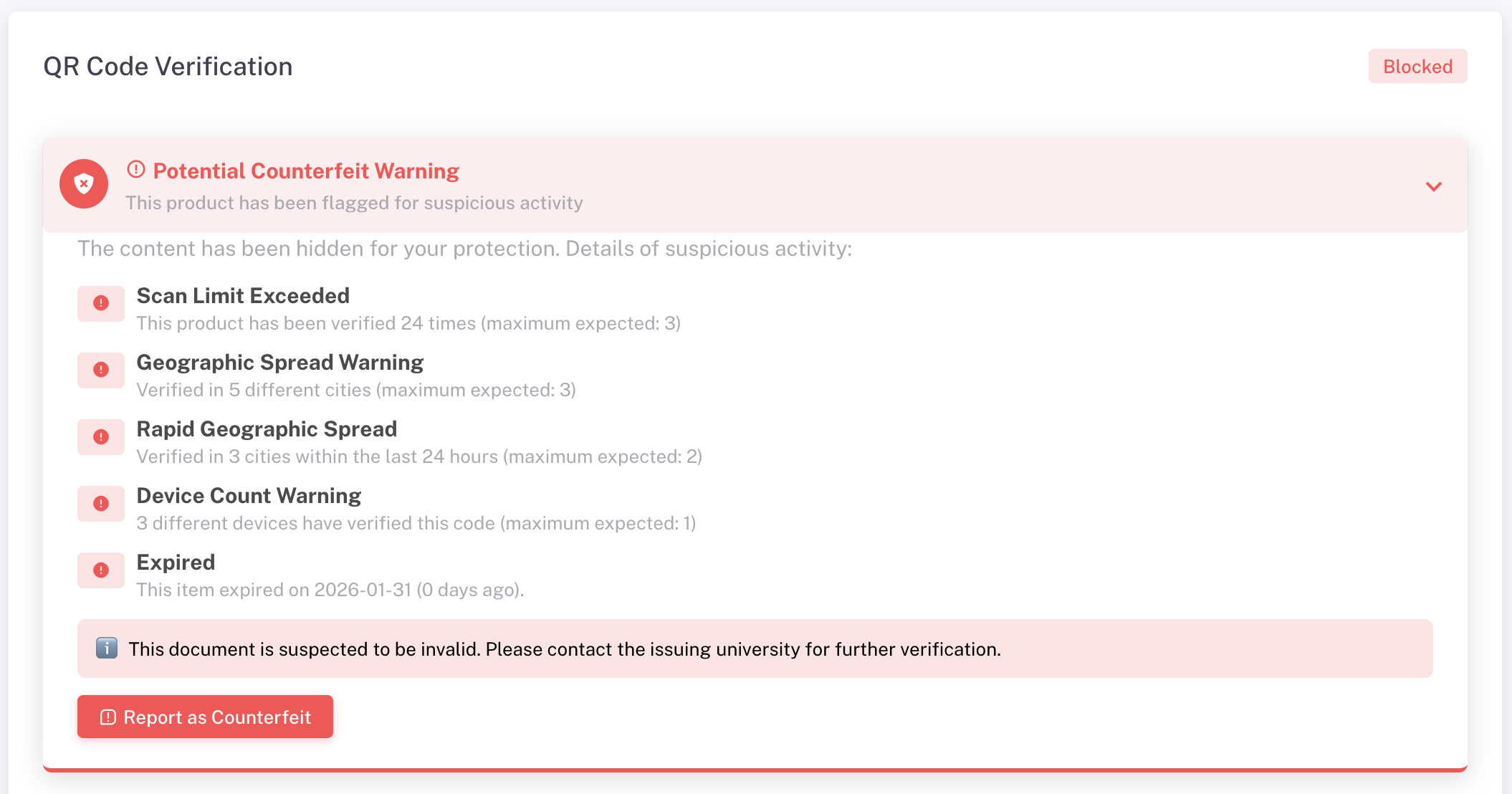
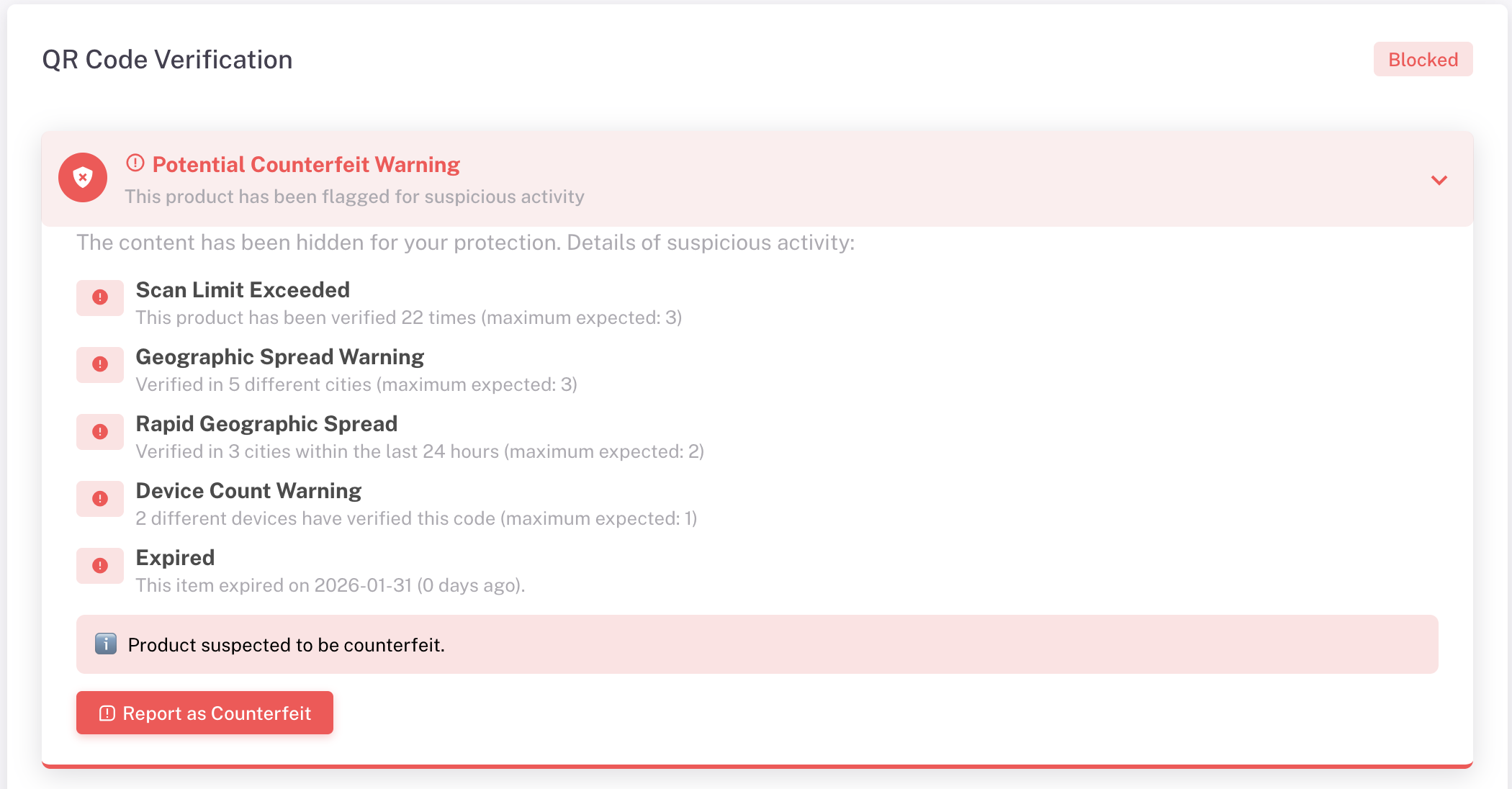
For additional security, GoValid integrates an Anti-Counterfeit feature designed to detect potential document misuse. The system does not simply display valid data—it actively monitors QR code scanning behaviour.
The system analyses whether:
- The same QR code is copied and used on multiple documents
- There is an unusually high number of scans
- Scans occur across multiple locations within a short time frame
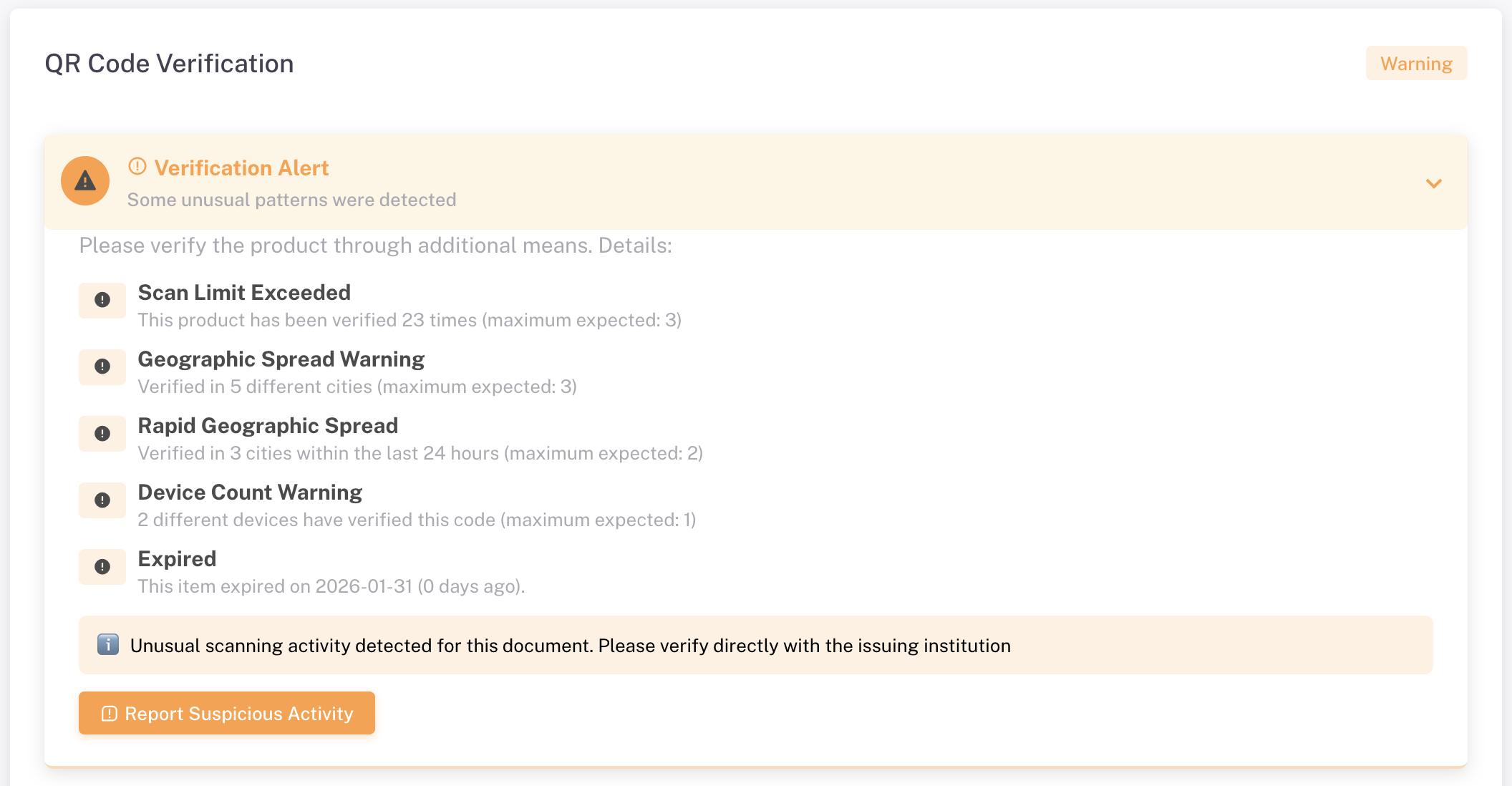
When suspicious patterns are detected, the system immediately displays a warning to the user scanning the document. The custom message may state like this:
“Unusual scanning activity detected for this document. Please verify directly with the issuing institution.”
Suitable Use Cases for QR-Based Digital Verification
QR-based digital signatures protected by GoValid Anti-Counterfeit are well suited for various academic documents, including:
- Training and course certificates
- Diplomas
- Letters of reference and official statements
- Thesis and dissertation approval pages
- Academic certificates and activity records
In short, the Anti-Counterfeit feature is essential for universities and institutions, as it enables early detection of forged diplomas, transcripts, and official documents circulating in the public domain.
Time to Move Toward Safer Digital Verification
Relying on handwritten signatures or scanned images is no longer a secure option in academic environments. By using QR codes connected to a validation system and protected by GoValid Anti-Counterfeit, document authenticity can be verified more reliably, while the risk of signature forgery is significantly reduced.








Comments are closed.